Sample sources glossary: Difference between revisions
From DM Live - the Depeche Mode live encyclopedia for the masses
Jump to navigationJump to search
(Created page with "250px|thumb|right|[https://www.wikiaudio.org/adsr-envelope/ Wiki Audio - ADSR Envelope] {| class="toccolours" cellspacing="2" style="float:le...") |
m (Majora101 moved page Template:Sample sources glossary to Sample sources glossary without leaving a redirect) |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 04:10, 20 August 2019
| Glossary | |
|---|---|
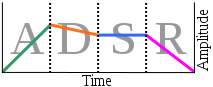
| ADSR - Abbreviation for Attack, Decay, Sustain, and Release. These are the four parameters found on a basic synthesizer or sampler envelope generator. Its function is to modulate some aspect of the instrument’s sound. | |
| Attack - How quickly the sound reaches full volume after the sound is activated (when the key is pressed). | |
| Crescendo - A gradual increase in the volume or intensity of a musical passage. | |
| Decay - How quickly the sound drops to its Sustain level after reaching its initial peak volume level. | |
| Delay (ADSR) - The span of time between a sound's initial keypress and when the sound activates. | |
| Delay (effect) - An electronically produced echo effect. | |
| Filter/cutoff - A circuit that eliminates certain harmonics from a sound generated by the sound source (the VCO, DCO etc), and allows the rest of the sound to pass. Using a filter/s to reduce harmonics provides timbre or colour to the sound. | |
| Loop - A sample of audio designed to play repeatedly. | |
| Loop point - The "coordinates" that define when a sample of audio is to loop. | |
| MIDI - A protocol that connects a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing and recording music. | |
| Oscillator - A circuit that generates a signal with a frequency in the audible range. This is the core of a synthesizer. A synthesizer can have one (monophonic), two (duophonic) or multiple (polyphonic/paraphonic) oscillators. Every oscillator can have a different waveform with each waveform having a distinct timbre. | |
| Panning - The left/right positioning of a signal within a stereo image. | |
| Release - How quickly a sound fades to silence when a note ends (the key is released). | |
| Resonance - Achieved by applying feedback to a filter: the effect of resonance “boosts” the frequencies around the cutoff frequency. As resonance increases, the feedback increases to a point that the filter can generate a sine-wave tone. This is called “self-oscillation”. | |
| Reverb - A naturally or electronically produced echo-like effect. Reverb is used to add a sense of space to a sound, creating the illusion of distance between the sound and the listener. | |
| Reverse - To play a sound backwards. | |
| Ring modulation - An effect where two waveforms are multiplied together with an output of the sum and difference of the frequencies present in each waveform. The effect is named for the metallic ringing timbre it creates | |
| Root key - In sampling, the root key of a sample is the key on which a sound plays at its given pitch. | |
| Sequencer - an instrument, either hardware or software, that uses control voltages, gate triggers and/or MIDI information to arrange events into musical patterns that can be played back programmatically. | |
| Sustain - The “constant” volume level the sound is to play at until it is released. | |
| Staccato - A musical passage or phrase performed with each note sharply detached or separated from the others. | |
| Transient - A high amplitude, short-duration sound at the beginning of a waveform that occurs in phenomena such as musical sounds, noises or speech. | |
| Transpose - To transfer to a different place or context. Musically, this can be to change from one key or note to another, or to play a sample of audio at a higher or lower pitch. | |
| Tremolo - A wavering effect in a musical tone, produced either by rapid reiteration of a note, by rapid repeated slight variation in the volume of a note, or by layering two notes of slightly different pitches to produce prominent overtones. | |
| Truncate - Often seen in samplers and waveform editors. To truncate is to shorten or remove part of a sound. | |
| Velocity - A data type that responds to the dynamic attack of a key press. This typically controls volume. In practice, a sound will change based on how forcefully a key is pressed. On a piano, pressing a key harder produces a louder, fuller sound. On many synthesizers, velocity can be assigned to modulate any number of settings, including pitch, panning, filters, etc. | |
| Vibrato - A rapid, slight variation in pitch in singing or playing some musical instruments, producing a stronger or richer tone. | |